猪场饮用水生物安全(三)- AASV 2020
来源:猪译馆 2020-05-26 15:16:57| 查看:次
译者的话<<
化学消毒剂的功效可以通过了解消毒剂的残留浓度和影响其消毒性能的因素(主要是温度、pH值、接触时间和所要达到的消毒水平)来预测。这一关系通常被称为CT,CT中的“C”是消毒剂的残留浓度(以mg/L计量),“T”是消毒剂接触时间(以分钟计量),这两个因素在特定条件下(如温度和pH值)针对特定的微生物就形成了CT这一理念。
CT可用于验证所用的消毒剂最佳消毒效果的浓度(毫克/升)、接触时间(分钟)和水的物理特性,如温度和pH值,以及用于日常确认和记录这些参数的方法(通过接受的标准方法,即美国标准试验方法进行验证)。
猪场饮用水生物安全(三)- AASV 2020
Groundwater Biosecurity for Livestock Production and Husbandry (Part 3) – AASV 2020
接上文......
公共供水系统的运营模式
Operative model for PWS’s<<
在安装消毒系统之前,公共供水系统需要向国家监管机构提交一份工程计划供审查和接受。这个计划必须包括设备规格和该设备已通过在一定的水环境、物理特性和流速范围内能达到并维持最低4 Log10(99.99%)的灭活/去除病毒的能力的验证(或者可以通过其他方式进行的验证)*。还要理解对病原体的去除率和/或灭活率越高,就意味着维持安全供水的可能性也越高。在公共供水系统行业中,4 Log10(99.99%)的去除率/灭活率在性能(生物安全性)、成本和复杂性方面达到了最大的平衡,并在一定程度上(可接受水平)可以防止病原体进入和/或在公共饮用水配水系统中繁殖扩散。
In advance of the installation of a disinfection system a PWS is required submit an engineering plan for State (regulatory) review and acceptance. This plan must include equipment specifications and validation that it has been, or otherwise can be *validated to achieve and sustain a minimum of 4 Log10 (99.99%) inactivation/removal of virus over a defined range of water conditions, composition and flow rates. Understanding, higher removal and/or inactivation rates translate to a higher probability of maintaining a safe water supply. Within the PWS industry, 4 Log10 (99.99%) removal/inactivation represents the greatest balance in regard to performance (Biosecurity), cost and complexity with an acceptable level of protection against pathogens from entering and/or proliferating in public drinking water distribution systems.
*在特定的规程下、用特定的方法、按照特定的检测目的而设的标准进行的第三方检测。
*Via third-party testing under protocols, methodologies, and standards accepted specifically for this specific purpose.
这个模型被称为CT概念,并用于验证所用的消毒剂最佳消毒效果的浓度(毫克/升)、接触时间(分钟)和水的物理特性,如温度和pH值,以及用于日常确认和记录这些参数的方法(通过接受的标准方法,即美国标准试验方法进行验证)。
This model is referred to as the CT Concept and is used for validation of disinfection efficacy in response to applied Disinfectant Concentration (mg/L) and Contact Time (minutes) and constituents of water composition, such as Temperature & pH and the means to confirm and record these parameters on a daily basis, via the use of accepted Standard Methods American Standard Test Method (ASTM).
消毒剂
Disinfectants<<
消毒剂量的测定
Determination of disinfection dose<<
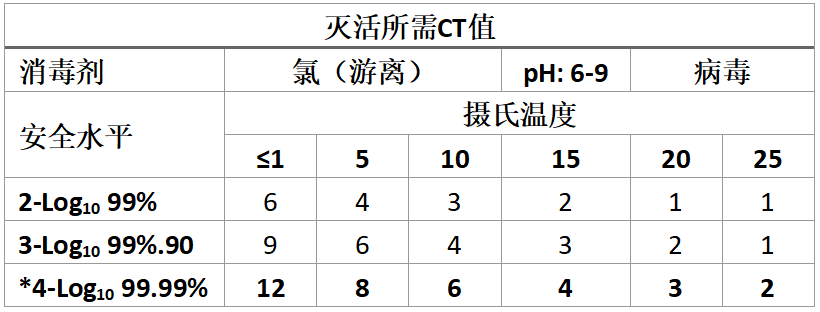
*饮用水系统所需的安全水平
*Required safety level (barrier) for potable drinking water systems
图5所示的设计消毒系统可以用如下方法进行验证:
A disinfection system of the design as described in Figure 5 can be validated as described below:
水力系数(每分钟20加仑的水消毒系统进行的示踪剂研究)= 0.5
Hydraulic Factor (by Tracer Study @ 20 gpm) = 0.5
水停留净时间(T) =(114加仑/20 gpm)×0.5 = 2.85分钟
Net Hydraulic Retention Time (T) = (114 gallons/20 gpm) ×.5 = 2.85 minutes
计算达到4 Log10灭活所需的游离氯浓度:
(CT值/时间) = mg/L
得到:6/2.85 = 2.11 mg/L
Calculation of Free Chlorine Concentration to achieve 4 Log10 Inactivation:
(CT Value/T) = mg/L
6/2.85 = 2.11 mg/L
图5:储水系统设计示例
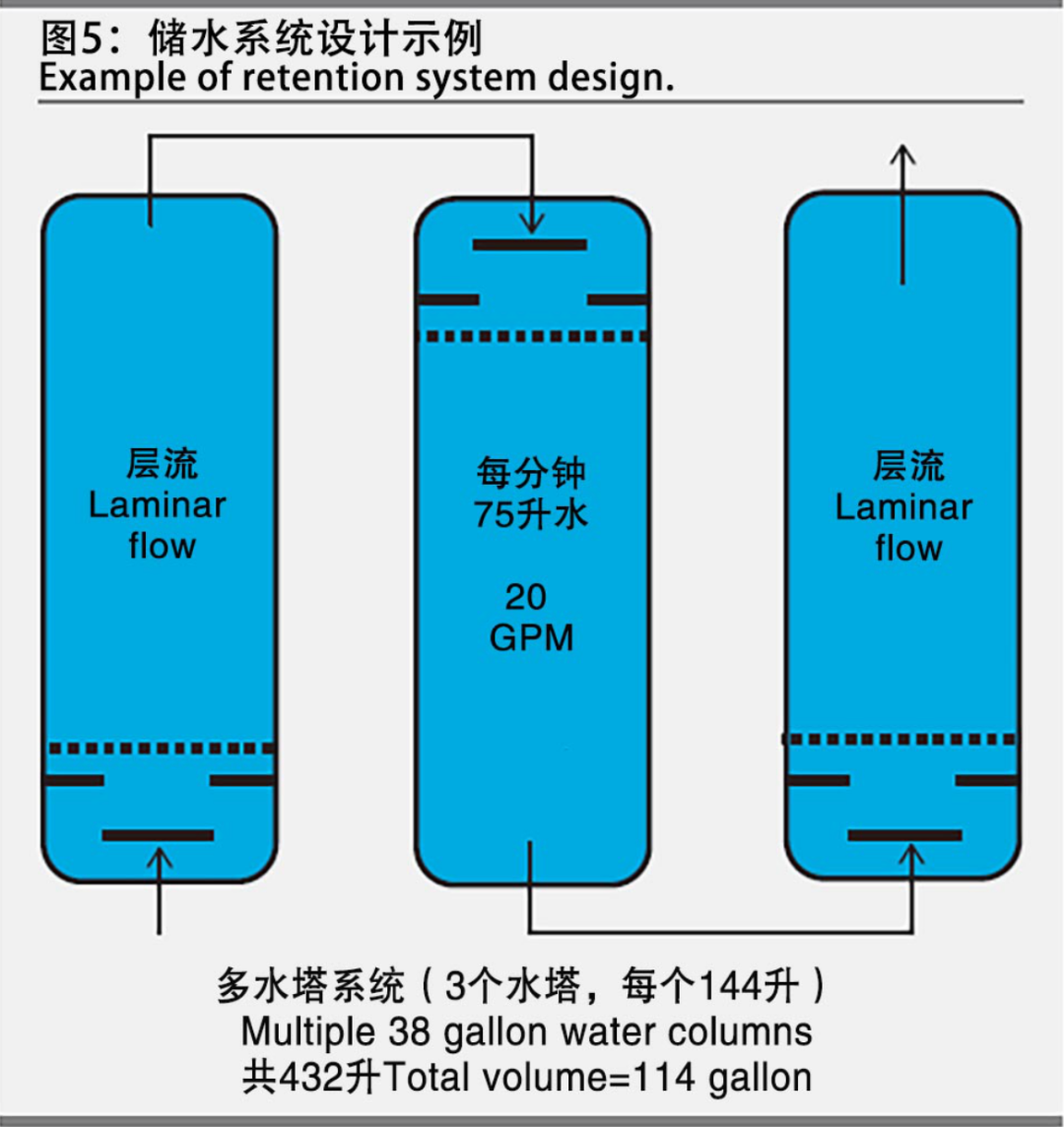
表5:使用游离氯灭活病毒的CT值,安全性较差
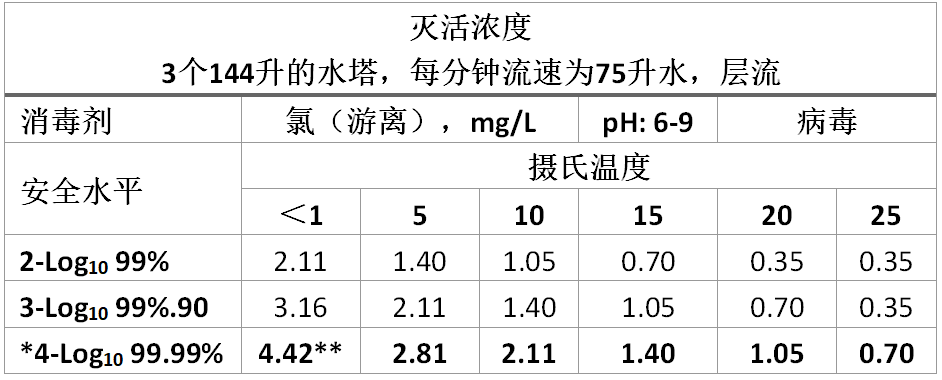
*饮用水系统所需的安全水平(屏障)
*Required safety level (barrier) for potable drinking water systems
**饮用水中的含量限值= 4.0 mg/L
**Concentration limit for potable drinking water = 4.0 mg/L
二氧化氯的参数如表6所示。
The same model applied for Chlorine Dioxide is shown in Table 6.
表6:二氧化氯对病毒的灭活CT值,pH 6.0-9.0
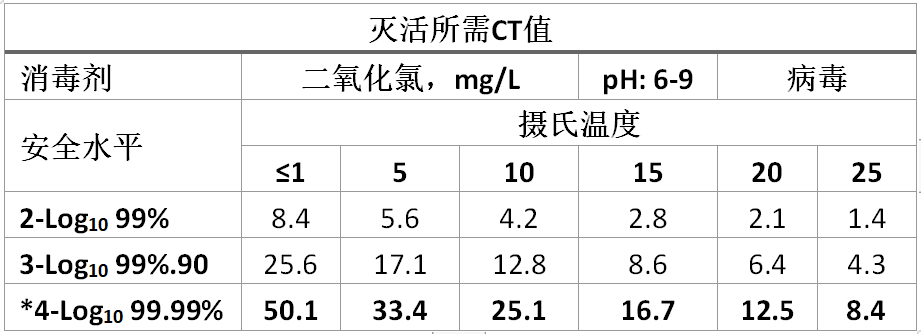
饮用水系统所需的安全水平(屏障)
*Required safety level (barrier) for potable drinking water systems
表7:使用二氧化氯灭活病毒的CT值,安全性较差
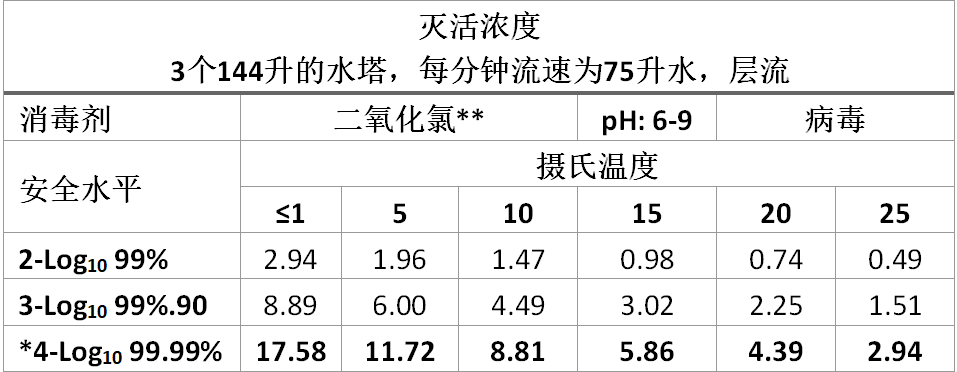
*饮用水系统所需的安全水平(屏障)
*Required safety level (barrier) for potable drinking water systems
未完待续……
服务热线:400-808-6188
Copyright©2010-2022 https://www.zhuwang.cc